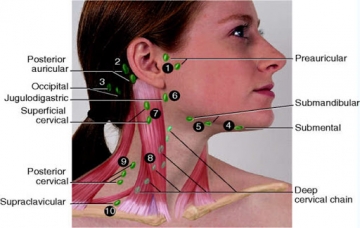
Lymph nodes are oval or round in shape. Their size can be from 1 mm to 2 cm. Lymph nodes belong to the body's immune system. They prevent the spread of germs, infections and cancer cells. In these nodes, special cells are formed lymphocytes, which are foreign and dangerous substances for the body and are actively involved in the destruction of cells. There are several groups of lymph nodes in the body. Thus, the lymph nodes are located in the elbow joint, under the armpit, in the knee joint, in the groin area. Lymph nodes in the neck protect the head and neck from infections and tumors. There are many lymph nodes in the abdomen and chest.
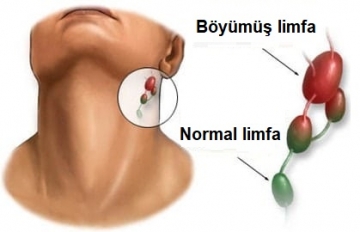
Lymphatic capillaries are present in all organs. Enlargement and inflammation of the lymph nodes anywhere in the body indicate a problem. Lymph node enlargement is usually caused by an infection, and in some cases by a tumor. Lymph node enlargement and inflammation are called lymphadenitis. Lymphadenitis may be purulent. The main symptoms of purulent lymphadenitis are enlarged and painful lymph nodes, redness of the skin in this area, fever, general weakness. If not treated in time (treated by a surgeon), purulent lymphadenitis can cause serious complications. In this case, the membrane of the lymph node is torn, and the accumulated pus spreads to the surrounding tissues. This is called phlegmon. In children, the lymph nodes grow more often.
Sometimes in children, the lymph nodes remain enlarged for a long time. In most cases, this is not an indication of a serious problem and is due to the immaturity of the child's immune system. However, if the child's lymph nodes remain enlarged for 1 month after the illness, see a pediatrician. Lymph nodes grow and become inflamed during acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis, dental abscess (purulent inflammation), pediatric infectious diseases (rubella, measles, mumps, mumps) and other infectious and bacterial diseases. In this case, the enlarged lymph nodes are soft and slightly painful to the touch. After a person recovers, the lymph nodes usually return to their normal size. Prolonged lymph node enlargement can be a sign of diseases such as brucellosis, listeriosis, mononucleosis and AIDS.
In some cases, an enlarged lymph node can be a sign of cancer. In tumors, cancer can directly damage the lymph nodes, or cancer that develops in other organs can metastasize to the lymph nodes. Lymphogranulomatosis and lymphosarcoma are the most common lymph node tumors. In these diseases, the lymph nodes grow to 3-4 cm and more, are hard and painless to the touch. Breast and abdominal lymph nodes are difficult enough to detect with cancer. Metastatic damage to the lymph nodes can be noted in various cancers. Tumor cells fall into the lymph nodes with the flow of lymph, where they begin to multiply, resulting in the growth of lymph nodes.
More often, lymph nodes metastasize to breast cancer, melanoma, thyroid cancer, cancer of the tongue and larynx, colorectal cancer, and lung cancer. At this time, the enlarged lymph node becomes firm and painless. Inguinal lymph node enlargement occurs in melanoma, vulvar cancer, and colorectal cancer. Breast cancer, melanoma, lymphogranulomatosis, etc. are associated with the growth of lymph nodes in the armpit area. can cause. Lymph nodes in the neck can grow in thyroid cancer, laryngeal cancer, tongue cancer, lymphogranulomatosis. Thus, enlarged lymph nodes can be a symptom of a very serious disease. Therefore, if you find an enlarged lymph node, be sure to consult a doctor.